Frenectomy
Frenectomy is a surgical procedure commonly performed in oral surgery to treat problems related to the oral brakes, which are bands of tissue located in the mouth. The brakes most commonly concerned by this procedure are the lingual brake (under the tongue) and the labial brake (between the upper or lower lip and the gum).
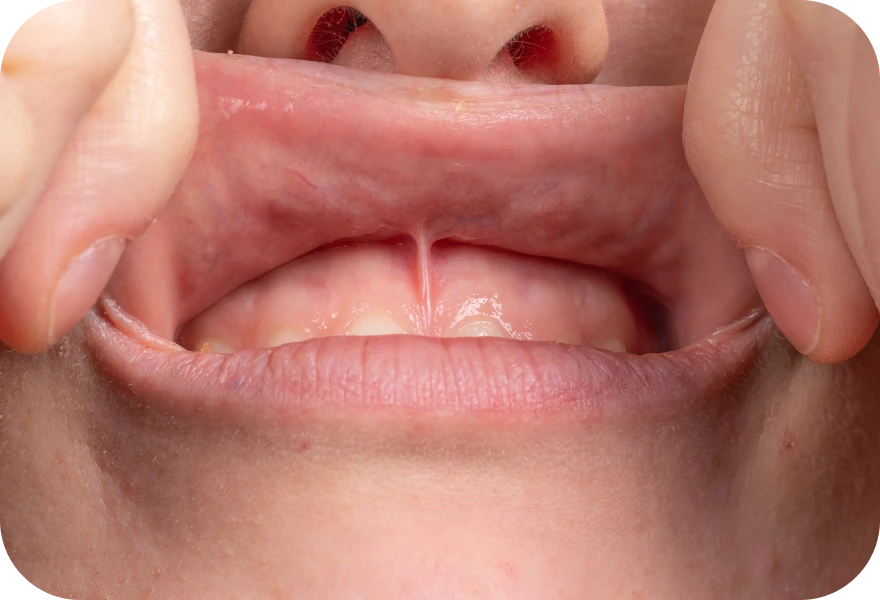
What is a frenectomy?
A frenectomy involves removing or modifying the involved frenulum when it is too short, causing functional limitations or dental consequences.
This procedure may be required for patients of any age, from infants to adults, depending on symptoms and complications.
What are the reasons for a frenectomy?
Patients rarely seek this type of treatment on their own, but are referred by their GP, paediatrician or sometimes speech therapist.
- Short lingual frenulum (ankyloglossia): A lingual frenulum that’s too short can restrict tongue movement, leading to difficulties in speaking, eating and, in infants, suckling properly.
- Prominent labial frenulum: An invaginated labial frenulum between the teeth can create a large gap between the front teeth (diastema) and contribute to orthodontic or periodontal problems.
- Pain and discomfort: Brakes that are too tight can cause pain and discomfort, especially when chewing or speaking.
- Orthodontic consequences: Prominent brakes can interfere with orthodontic treatment and prevent teeth from moving properly.
The frenectomy procedure
- Initial consultation: The first step is an evaluation by Dr. Arnaud, which includes a clinical examination and possibly x-rays (to assess bone level in cases of gingival recession) to understand the anatomy of the brake and its effects.
- Surgical procedure: Frenectomy is usually performed under local anaesthetic, although sedation options may be available for anxious patients or children/infants.
- The surgeon uses surgical instruments to cut the brake. The procedure is fast and generally minimally invasive.
- Post-operative care and follow-up: After the procedure, absorbable sutures may be placed. Post-operative instructions will be provided in consultation to ensure an ideal, uncomplicated recovery. A follow-up appointment will be scheduled at 10 days to monitor the progress of the wound.
Obligatory rehabilitation after frenectomy
For any lingual frenectomy (of the tongue frenulum) in adolescents and/or adults, re-education by a speech therapist in the week following the surgical procedure is mandatory to avoid recurrence.
This re-education allows us to work on lingual amplitude, improve phonation and swallowing after the operation, and maintain the result.