Zygomatic implants
Zygomatic implants are medical devices used in oral implant surgery to provide a prosthetic fixation solution for patients with severe bone resorption in the upper jaw.
Unlike conventional dental implants, which are anchored in the alveolar bone of the jaw, zygomatic implants are longer and are inserted into the zygomatic bone, the bone that forms the cheekbones.
This technique makes it possible to bypass major bone deficits without the need for bone grafting, and to give patients the possibility of having “fixed” teeth despite the small amount of bone present.
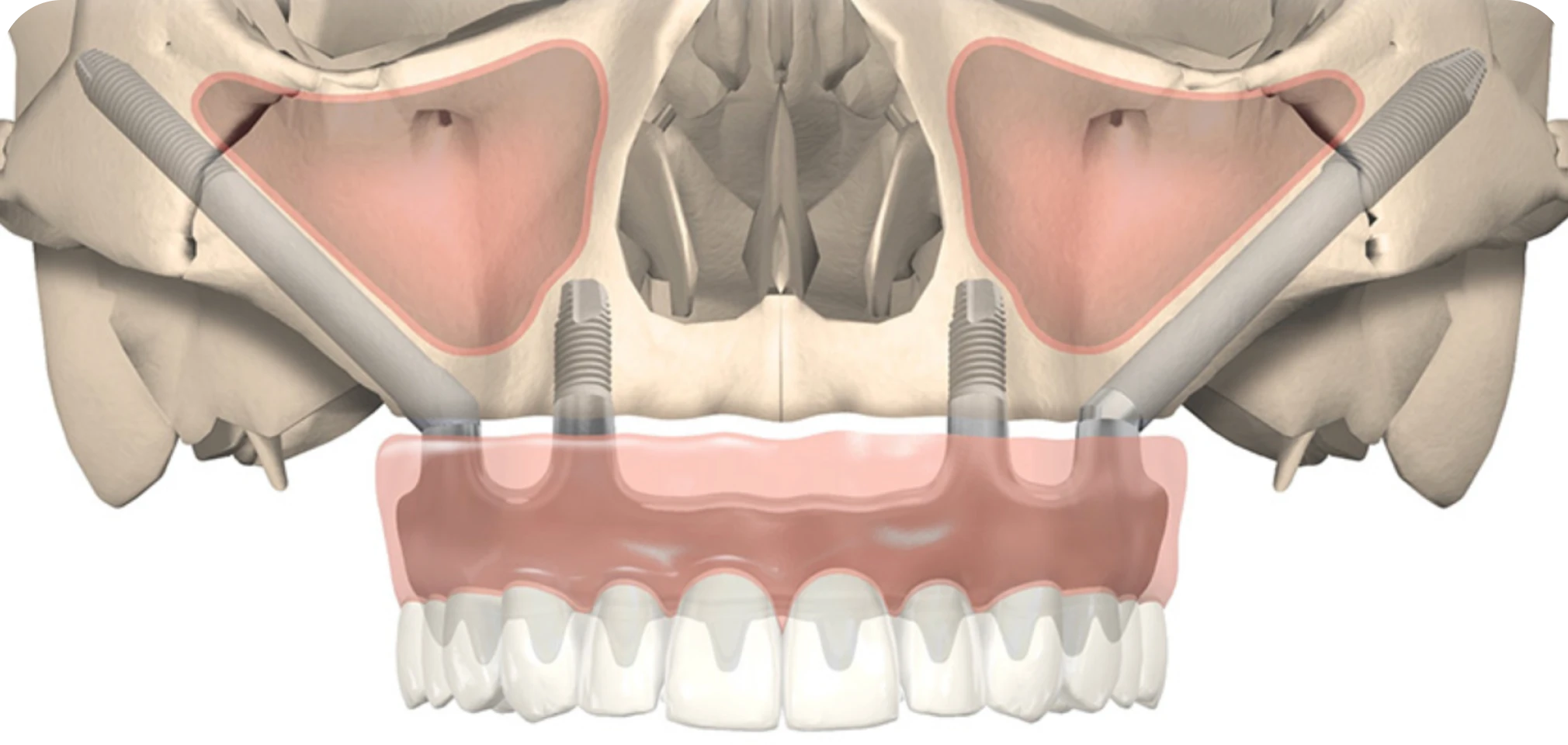
Who can receive zygomatic implants?
Zygomatic implants are mainly indicated in the following situations:
- Severe maxillary bone atrophy: Patients with advanced bone loss in the upper jaw where conventional implants cannot be stabilized. Bone loss can be caused by several mechanisms: cyst, trauma, benign tumor surgery, malignant tumor surgery, advanced periodontitis with loosening of the teeth, teeth removed several years ago…
- Conventional implant failures: Patients who have had repeated failures with conventional implants due to insufficient bone quality.
- Medical conditions or age limiting bone grafts: Patients for whom bone grafts are not recommended or desired.
What is the surgical procedure for zygomatic implants?
The zygomatic implant procedure is more complex than traditional implants and requires additional expertise. Here are the main steps:
Preoperative evaluation :
Includes clinical examination, X-rays and cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) to assess the bone structure of the zygomatic bones and the condition of the maxillary sinuses.
Surgery:
Usually performed under general anaesthetic or deep sedation, the implant is inserted through the alveolar ridge and directed into the zygomatic bone. The implant position can be internal, external or straddling the maxillary sinus, depending on the initial shape of the bone. Implant length can be varied to suit the specific anatomy of each patient.
An immediate loading protocol is very often associated with this, where the patient’s existing prosthesis (or the one made for the day of the operation) is attached directly to the implants. This allows the patient to leave with fixed teeth.
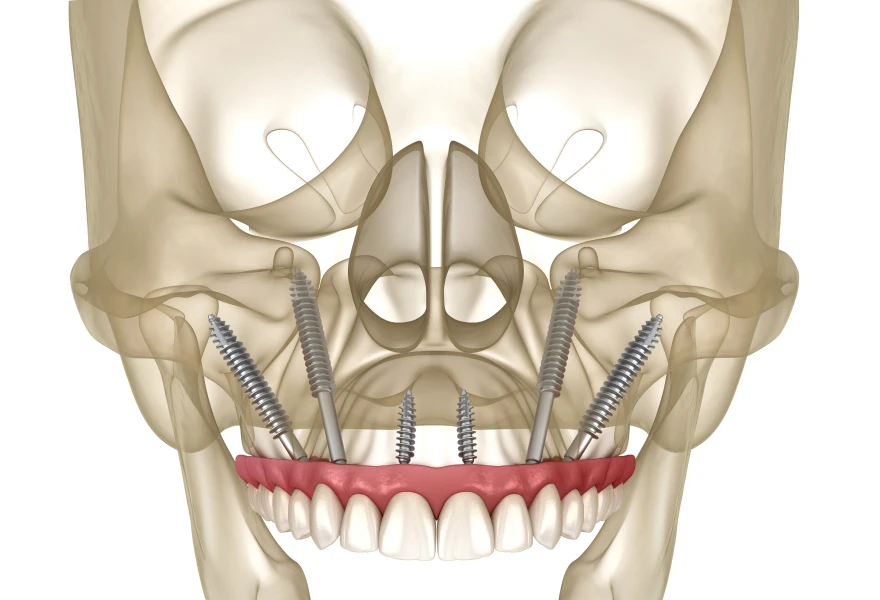
Follow-up and post-operative care:
The post-operative period requires special attention, with regular checks to monitor healing and implant integration.
In the case of implant-supported dental prostheses, checks and modifications are carried out with the general dental practitioner.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of zygomatic implants?
Advantages of zygomatic implants
- Alternative to bone grafting: By avoiding bone grafting procedures, zygomatic implants reduce the risks and complications associated with these operations.
- Rapid rehabilitation: Patients can often receive a temporary fixed prosthesis soon after surgery, improving masticatory function and aesthetics more quickly. For example: a treatment plan including bone grafting adds between 6 and 9 months of healing time.
- High success rates: studies show high survival rates for zygomatic implants, even in unfavorable bone conditions, with rates ranging from 95% to 98% over a period of 5 to 10 years. They also show a significant improvement in patients’ quality of life, particularly in terms of masticatory function and aesthetics in cases where traditional implantology was impossible.
Considerations and risks
Technical complexity: Zygomatic implant surgery is a demanding technique, with short-, medium- and long-term complications that are more invasive than traditional implants.
This is why surgery under local anaesthetic is most often not recommended.
Potential complications: Complications can include maxillary sinusitis, infection, paresthesia (reduced sensitivity of the cheek skin) and problems with prosthesis fixation.
Zygomatic implants represent an advanced solution for oral rehabilitation in patients with severe maxillary bone resorption. This technique offers a viable alternative to bone grafting, with satisfactory clinical results. For more information or to discuss your specific situation in consultation with Dr. Arnaud. Thorough evaluation and personalized planning are crucial to the success of this complex procedure.